Introduction to Dow Theory
Dow Theory is a type of technical analysis developed by Charles Dow, the co-founder of Dow Jones & Company and The Wall Street Journal. This theory is based on his collection of editorials discussing the stock market. While Dow himself never used the term “Dow Theory,” it was later coined by others who had interpreted and compiled his thoughts.
Dow Theory provides a framework for understanding and predicting market price movements. It is based on the premise that the market has three types of movements: primary trends, secondary trends, and minor trends.
Components of Dow Theory
Primary Trends
The primary trend is the major market direction over the years, which can be either bullish (upward) or bearish (downward). This trend is often referred to as the “tide” in the analogy of the sea.
Secondary Trends
Secondary trends are corrections to the primary trend and can last from a few weeks to a few months. In the sea analogy, these would be the waves that form with the tide.
Minor Trends
Minor trends are short-term fluctuations that last from hours to a month. These are equivalent to the ripples on the waves in the sea analogy.
Principles of Dow Theory
Dow Theory is based on six basic principles:
The Market Discounts Everything
The theory assumes that all information – past, present, and even future – is reflected in the market price. Therefore, the market price is more significant than the underlying fundamentals of the economy or a particular company.
There are Three Types of Market Trends
As mentioned earlier, Dow identified three types of trends: primary, secondary, and minor. Each of these has a different timescale and significance.
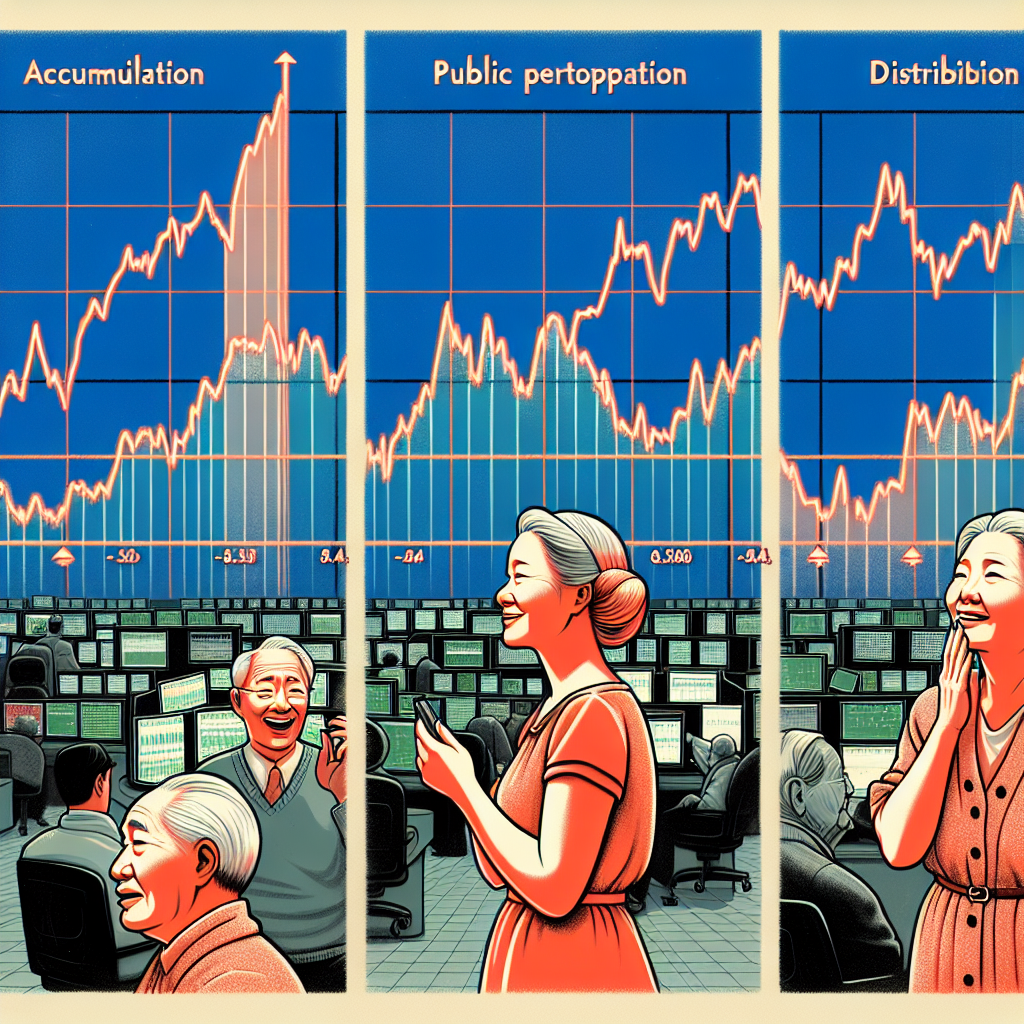
Primary Trends have Three Phases
Dow suggested that primary trends have three phases: accumulation, public participation, and distribution. The accumulation phase is when informed investors start to buy or sell, the public participation phase is when the majority of traders follow, and the distribution phase is when informed investors start to do the opposite.
The Stock Market Indices Must Confirm Each Other
In Dow’s time, he focused on two indices: industrial and rail. He believed that for a primary trend to be valid, both indices must confirm each other.
Volume Confirms the Trend
Volume should increase in the direction of the primary trend. For example, in an uptrend, volume should increase when prices rise and decrease when prices fall.
Trends Exist Until Definitive Signals Prove They Have Ended
According to Dow, trends will continue until there are clear signs that they have ended. This principle emphasizes the importance of identifying trend reversals.
Application of Dow Theory in Market Forecasting
Dow Theory is a tool used by traders to analyze the market’s direction. By identifying the primary, secondary, and minor trends, traders can make educated predictions about future market movements.
While Dow Theory is not a guaranteed method of forecasting, it provides a solid foundation for understanding market trends. It can help traders make informed decisions about when to buy or sell securities.
In conclusion, Dow Theory is a valuable tool in market forecasting. By understanding its principles and applying them correctly, traders can gain a better understanding of market trends and make more informed trading decisions.